On this page
Introduction
More information on Locators and using them in the ArcGIS platform can be found in the ArcGIS Online Help.
A locator is a snapshot of data that will help you to find a specific location on the map or generate features from tables of addresses or places. A locator can be used to find a specific location or generate point features from tables of addresses or places.
Terminology
- Geosearch is searching for and locating an address or location on a map.
- Geocoding is where an address or place is converted to a set of coordinates (x,y) and generally creating a new feature based on that or appending that information to an already existing record.
- Batch geocoding is Geocoding for a large number of locations at once, typically, a table of addresses or locations.
- Reverse Geocoding is where a set of coordinates is converted to an address that is at, or the closest to, that point. e.g. you click on a map and it tells which address you have clicked on.
With the tool you can build a variety of locators from different data sources. This includes:
- AddressBase Core
- AddressBase Premium
- AddressBase Premium Islands
- OS NGD Address
- CAG
- LLPG
Using the tool
Locate the UK Locators Toolset and run the script for the dataset you wish to use.

AddressBase Premium or AddressBase Premium Islands locators
For AddressBase products enter the location of the Geodatabase where the AddressBase featureclasses and tables exist.
NB: This data will need to have been created using the UK Data Loader AddressBase loading tool.

Once you have selected your datasource it will present you with a list of the prefixes for the AddressBase data it has found at that location. You will need to select the one you wish to build the locators from.
Enter the Destination Folder where the Locators are to be created. It is worth naming this folder in relation to the AddressBase Epoch it relates to. Ideally, it should be an empty folder.
For AddressBase Premium data you are also presented with a tick box entitled “Create all locators” which is ticked by default. If you untick this option you will have various options to configure the locators you are creating. The options are:
- Do not create UPRN locator
- Do not create Postcode locator
- Do not create Street locator
- Do not Create Local Authority Locators
- Do not Create Royal Mail Locators
- Do not create Historic (Local Authority) Locators
- Do not Create Provisional (Local Authority) Locators
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
AddressBase Core Locators
For AddressBase products enter the location of the Geodatabase where the AddressBase featureclasses and tables exist.
NB: This data will need to have been created using the UK Data Loader AddressBase loading tool.

Once you have selected your datasource it will present you with a list of the prefixes for the AddressBase data it has found at that location. You will need to select the one you wish to build the locators from.
Enter the Destination Folder where the Locators are to be created. It is worth naming this folder in relation to the AddressBase Epoch it relates to. Ideally, it should be an empty folder.
For AddressBase Core data you are also presented with a tick box entitled “Do not create Postcode Locators” which is unticked by default. If you tick this option you will have the option to not create the postcode locator.
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
NGD Address Locator
For NGD Address products enter the location of the GeoPackage containing the NGD Address data.
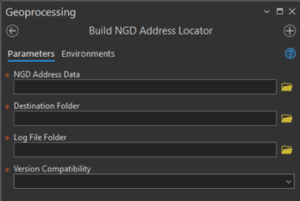
Enter the Destination Folder where the Locators are to be created. Ideally, it should be an empty folder.
Select the folder where the log file will be created.
Finally, you will then need to select the version of locator to be created.
- Current Version – This will create a locator using the latest version of the locator format. This version requires ArcGIS Enterprise version 11.4 or later if you wish to publish the locator as a geocoding service.
- 3.0 – 3.3 – This will create a locator based on the ArcGIS Pro 3.0-3.3 format. Select this version if you wish to publish the locator as a geocoding service in ArcGIS Enterprise version at 11.0 – 11.3
LLPG and CAG locators
There are multiple tools available for the LLPG and CAG datasets.
Create a Locator direct from a gazetteer extract
If you have the source data in DTF/SDTF format and just wish to create a locator from it then each has a tool called “Load Data and Build Locator”
For LLPG and CAG data enter the location of the DTF or SDTF to be used.

Enter the source data folder which contains your DTF/SDTF files.
Enter the Destination Folder where the Locators are to be created. Ideally, it should be an empty folder.
You will then be presented with a tick box entitled “Create all locators” which is ticked by default
If you untick this option you will have various options to configure the locators you are creating. The options are:
- Do not create UPRN Locators
- Do not create Postcode Locators
- Do not create Street Locators
- Do not create Historic Locators
- Do not Create Provisional Locators
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
Loading data, applying COUs and building locators as separate tools
Alternatively if you wish to apply COUs on a regular basis then firstly you will need to load an initial load of all the data into a file geodatabase using the relevant “Load Data” tool. You can then subsequently apply COUs using the “Process COU” tool. Once you have a loaded, or updated, file geodatabase then you can use the “Build Locator from Pre-loaded Data” tool
Load Data
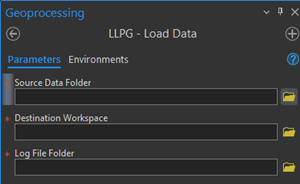
Enter the source data folder which contains your DTF/SDTF files.
Enter the Destination Folder where the file geodatabase will be created.
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
Process COU
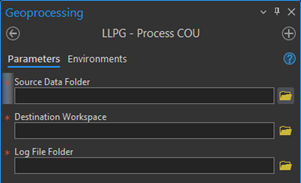
Enter the source data folder which contains your DTF/SDTF files.
For the Destination Workspace, select the file geodatabase against which the COU will be applied
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
Build Locator from Pre-loaded Data
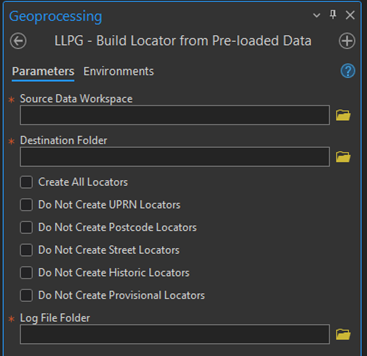
Enter the source data folder which contains your DTF/SDTF files.
Enter the Destination Folder where the Locators are to be created. Ideally, it should be an empty folder.
You will then be presented with a tick box entitled “Create all locators” which is ticked by default
If you untick this option you will have various options to configure the locators you are creating. The options are:
- Do not create UPRN Locators
- Do not create Postcode Locators
- Do not create Street Locators
- Do not create Historic Locators
- Do not Create Provisional Locators
Finally you will then need to select the folder where the log file will be created.
What does the tool do?
The tool will create LOC, LOZ and loc.xml files for each locators type. The Build Locators tool organises these categories of addresses into a number of locators to enable searching against some or all of the lifecycle elements or alternative addresses.
The tool builds up to 9 locators, dependent on the data and the options selected; the default option is to build all locators.
All locators are designed so that as well as searching by address you are also able to search by UPRN for specific records. The only two which differ from this is the street locator which allows you to search by street or by USRN and the postcode locator which only allow you to search on postcode and return a full list of addresses.
AddressBase Core Locators
For full details of the AddressBase Core please refer to the Ordnance Survey’s Technical Specification which is the definitive definition in the event of any confusion or apparent contradiction.
Running the Build AddressBase Core Locators tool will create two locators.
abcore_address_locator.loc
This locator contains all Local Authority current and alternative addresses. This includes the equivalent language (Welsh, Gaelic, English) addresses.
postcode_locator.loc
This locator contains all Local Authority current and alternative addresses. This includes the equivalent language (Welsh, Gaelic, English) addresses. It allows you to search for all these addresses using the postcode.
AddressBase Premium
For full details of the AddressBase Premium please defer to the Ordnance Survey’s Technical Specification which is the definitive definition in the event of any confusion or apparent contradiction.
Running the Build AddressBase Premium Locators tool will create multiple locators, or a subset depending on the options selected.
abprem_la.loc
This locator contains all Local Authority current and alternative addresses. This includes the equivalent language (Welsh, Gaelic, English) addresses.
abprem_la_hi.loc
This locator contains all Historic Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
abprem_la_pv.loc
Locator contains all Provisional Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
abprem_rm.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these.
abprem_uprn.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by UPRN.
abprem_post.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by Postcode
abprem_street.loc
Locator contains all street information supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by street name or USRN
Composite locators
There are two composite locators which are used to combine the locators above into a single locator endpoint that you can query.
os_addressbasepremium_all_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search all the records in the data. This includes details of properties which no longer exist (historic) and addresses which are not yet built (provisional).
It is a composite of the following locators:
- abprem_rm
- abprem_la
- abprem_la_hi
- abprem_la_pv
os_addressbasepremium_curr_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search for only current addresses. This is so you can have a locator where you can search just for addresses that exist now.
It is a composite of the following locators:
- abprem_rm
- abprem_la
AddressBase Premium Islands Locators
For full details of the AddressBase Premium Islands please defer to the Ordnance Survey’s Technical Specification which is the definitive definition in the event of any confusion or apparent contradiction.
Running the Build AddressBase Premium Locators tool will create multiple locators, or a subset depending on the options selected.
abisland_la.loc
This locator contains all Local Authority current and alternative addresses. This includes the equivalent language (Welsh, Gaelic, English) addresses.
abisland_la_hi.loc
This locator contains all Historic Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
abisland_la_pv.loc
Locator contains all Provisional Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
abisland_rm.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these.
abisland_uprn.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by UPRN.
abisland_post.loc
Locator contains all addresses supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by Postcode
abisland_street.loc
Locator contains all street information supplied by the Royal Mail and equivalent language versions of these searchable by street name or USRN
Composite locators
There are two composite locators which are used to combine the locators above into a single locator endpoint that you can query.
os_addressbasepremiumislands_all_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search all the records in the data. This includes details of properties which no longer exist (historic) and addresses which are not yet built (provisional).
It is a composite of the following locators:
- abisland_rm
- abisland_la
- abisland_la_hi
- abisland_la_pv
os_addressbasepremiumislands_curr_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search for only current addresses. This is so you can have a locator where you can search just for addresses that exist now.
It is a composite of the following locators:
- abisland_rm
- abisland_la
NGD Address Locator
For full details of NGD Address please refer to the Ordnance Survey’s Technical Specification which is the definitive definition in the event of any confusion or apparent contradiction.
Running the Build NGD Address Locator tool will create one locator.
ngd_built_address_locator.loc
This locator contains all of the current physical addresses from the NGD address data.
CAG Locators
For full details of the Corporate Address Gazetteer please refer to the Scottish Gazetteer Conventions documentation.
Running the Build CAG Locators tool will create multiple locators, or a subset depending on the options selected.
cag_curr.loc
This locator contains all Local Authority current and alternative addresses.
cag_hi.loc
This locator contains all Historic Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
cag_pv.loc
This locator contains all Provisional Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
cag_uprn.loc
This locator contains all addresses searchable by UPRN.
cag_post.loc
This locator contains all addresses searchable by postcode.
cag_street.loc
This locator contains all streets searchable by street name or USRN.
Composite locator
There is also a composite locator which is used to combine the locators above into a single locator endpoint that you can query.
cag_all_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search all the records in the data. This includes details of properties which no longer exist (historic) and addresses which are not yet built (provisional).
It is a composite of the following locators:
- cag_curr
- cag_hi
- cag_pv
- cag_uprn
LLPG Locators
For full details of LLPG please defer to the Geoplace Technical Specification which is the definitive definition in the event of any confusion or apparent contradiction.
Running the Build LLPG Locators tool will create multiple locators, or a subset depending on the options selected.
llpg_curr.loc
This locator contains all current and alternative addresses.
llpg_hi.loc
This locator contains all historic addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
llpg_pv.loc
Locator contains all Provisional Local Authority Addresses, and any equivalent language versions of these.
llpg_uprn.loc
This locator contains all addresses searchable by UPRN.
llpg_post.loc
This locator contains all addresses searchable by postcode.
llpg_street.loc
This locator contains all streets searchable by street name or USRN.
Composite locators
There are two composite locators which are used to combine the locators above into a single locator endpoint that you can query.
When searching where suggestions are enabled, candidates will be suggested from all locators.
When batch geocoding, addresses will be matched to any available candidates from the first locator in the composite, in the order given above, to return a single candidate.
llpg_all_address_locator.loc
This locator can be used to search all the records in the data. This includes details of properties which no longer exist (historic) and addresses which are not yet built (provisional).
It is a composite of the following locators:
- llpg_curr
- llpg_hi
- llpg_pv
- llpg_uprn
How to use Locators
Once a locator has been created you can then decide what to do with that locator such as using it in ArcGIS Online, ArcGIS Pro or ArcGIS Enterprise/Server.
Using a Locator within ArcGIS Pro
Add a locator in ArcGIS Pro
You can use the locator immediately in ArcGIS Pro by adding the local locator to your project. Do this by right clicking on the Locators folder in your project and navigating to your locator

Locate
Open your map and in the Inquiry group click on the Locate button. This will open the Locate pane. Your locator will be enabled automatically but you can modify which locators are being used by selecting them in the drop down list.

Start tying your address and suggestions will be begin to appear. Note: If you are searching multiple locators, the name of the locator the results are returning from will be in bold

You can then select the suggestion you are looking for and the map will pan and zoom to that location and add a location on the map

Reverse Geocode
On the map
Right click on your map and select “What’s here?”


For a table
To reverse geocode a table of points you can use the Reverse Geocode Geoprocessing tool
Batch Geocode
On the map
Right click on your table in the Table of Contents and select “Geocode Table”

You will then be guided through a wizard to geocode the table. More details can be found in the ArcGIS Pro help.
For a table
To batch geocode a table of locations you can use the Geocode Addresses tool
Using a locator within ArcGIS Online
To use your Locator within ArcGIS Online you will first need to publish your locator to your own ArcGIS Enterprise or ArcGIS Server.
You will then need to add that locator as an item within your ArcGIS Online Content. When you add the item, if your locators is not public, then it will ask you to enter some credentials. These will be credentials of a user within your ArcGIS Enterprise/Server that has access to that locator.
Once added as an item you will then add that locator to your Utility Services within your Portal.
The online help gives full details on how you can set this up. Once you have the locator added it will then appear in your dropdown lists of locators and can be used in your Maps and Web Apps.
If you plan to add the locator into any applications which are then made public you will need to share the item appropriately and where needed utilise the Limit Usage options within ArcGIS Online.
Publishing to ArcGIS Enterprise or Stand-alone ArcGIS Server
One common workflow is to publish that locator as a service in ArcGIS Enterprise or ArcGIS Server. Please note there are two different workflow one for sharing locators to ArcGIS Enterprise the other publishing a geocoding service to a stand-alone ArcGIS Server, they do the same thing just slightly different methodology. There is also a minimum specification for ArcGIS Server of 10.8.1 or higher and ArcGIS Enterprise of 10.9.1 or higher to be able to publish the locators created using UKDL.
Having done this, the locator can then be made available to be used in your Web apps, ArcGIS Desktop and ArcGIS Online.
It is recommended that if you are going to publish and share your locator these ways that you store it on the server, you can then register the folder location as a data store. If you do not use a registered data store then the locator (and all of its sublocators) will be copied to the server.
Details on sharing and the advantages of using a registered data store can be found in the ArcGIS help.
Once published you will then add that locator to your Utility Services within your Portal.
The online help gives full details on how you can set this up. Once you have the locator added it will then appear in your dropdown lists of locators and can be used in your Maps and Web Apps.
If you plan to add the locator into any applications which are then made public you will need to share the item appropriately and where needed utilise the Limit Usage options.
Ordering of results
Geosearching
When searching using the composite locator, candidates will be suggested from all locators in order of the locator.
Batch Geocoding
When batch geocoding using a composite locator, the system will search each locator in turn and if the address is matched it will stop at that point and return the match from that locator.
In the case of the AddressBase Premium composite locators (where you have chosen the default options) it will first search the Royal Mail locator. If it finds a match then that is the one it will return and use. If however it does not find a match it will then move on to the Local Authority locator and search that for a match and so on for the historic addresses and then provisional addresses.
Results based on map extent
Locators are designed to favour addresses within the extent you are viewing on a map and this will affect the results you see when searching.
For example if you are viewing the North East of England on a map and search for “High Street”, you will get one set of results based in that map extent.

However, if you were zoomed in to Durham, the same query produces a different set of results, focused on Durham

